Baidu Updates Project Aimed at Protecting Original Content

Anyone with quality original content on the web likely knows the constant nuisance of scraper sites that grab and repost your content without attribution, claiming to be the original creator. Even worse is the infrequent, but real occurrence of when these sites actually outrank your original content. Unfortunately, nowhere is this phenomenon more of an issue than in China.
Back in 2013, Baidu launched what it called the Spark Project (百度星火计划), as an initiative aimed to combat the deluge of stolen, spun and low quality content on the web. The project consists of algorithm updates to allow Baidu better distinguish between original content and stolen or spun content. Baidu has been working with a subset of qualified websites to participate in the project’s experiments, offering incentives to participants such as:
• Prioritized ranking in search results
• Tag that says “Original” next to search result snippet
• Prioritized ranking in Baidu News
• Advanced webmaster tools
After the first batch of promotion and press releases, the Spark Project has been relatively quiet for almost 2 years until recently, Baidu announced more details of the new Baidu Spark Project 2.0.
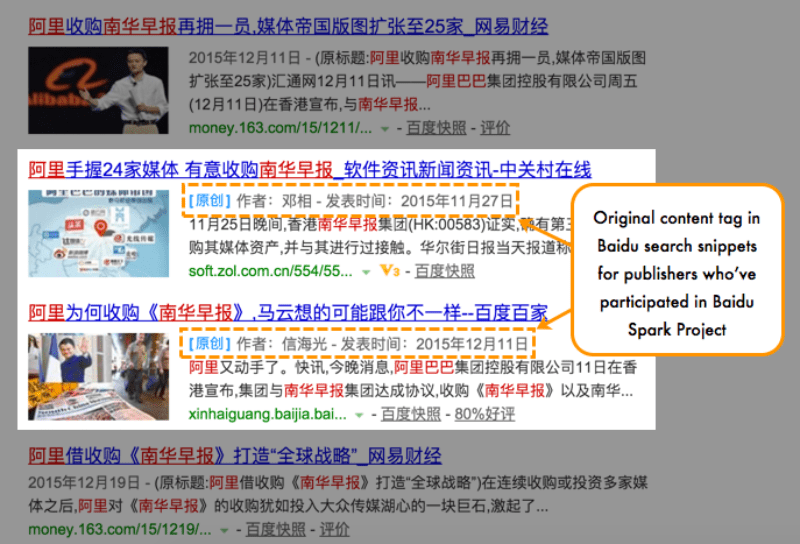
The intent and concept of Spark Project 2.0 is basically the same as 1.0. In Baidu’s recent announcement, they outlined their definition of original content and a set forth implementation standards for webmasters to comply with the 2.0 project.
Just like 1.0, the new project is still in closed beta, focused on data collection and original content recognition on news sites, blogs with technical how-to guides, tutorials, travel related content, and other similar article types.
According to Baidu, the project will open for public beta very soon. We believe this project is going to be very important for those who create original content targeting Chinese audiences, so let’s take a moment to understand this announcement in more detail.
Baidu provided a definition of what they consider original content:
From Baidu:
原创,与现代社会人们理解的概念一致,是指独立完成创作的作品。百度确认的原创是指:由个人或团队独立创作,且内容唯一的作品
采用歪曲、篡改他人创作,抄袭、剽窃他人创作等手段完成的“作品”,不属于原创,也就是俗称的伪原创。同时也不能称之为改编、翻译、注释。(当然把外文翻译成中文,我们是鼓励的!)
Translation:
Unique content is completed independently by an individual or team
Distortions or mutilations of others’ creations, or plagiarized content won’t be considered original, and will not be considered as adaptations, translations, or annotations. Of course, translations from other languages to Chinese are encouraged.
As the 2.0 project is still in closed beta, implementing these guidelines probably won’t have the same effect as if your site was a participant of the project. However, we still recommend following these guidelines, as they are common-sense principles for creating good-quality content, and your site will be ready once the project eventually opens to every site.
Information about publish date, author and source needs to be clearly shown in the body section of the page, regardless of desktop or mobile site. Baidu recommend this information to be placed below the main heading elements.
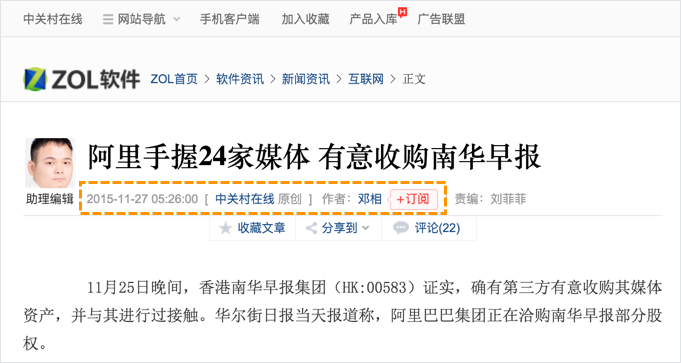
Just placing the publish date, author and source information in the body text is not enough. This information will also need to be inserted as meta tags as below, take this article in our blog as example:
// This is a mandatory and fixed entry
og:type” content=”article“/>// The earliest published time, this is mandatory and doesn’t required to be shown in the body of the page, the entry format needs to comply with ISO8601 regulations’ UTC format like “YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS+TIMEZONE”
article:published_time” content=”2016-01-26T09:37:23+08:00” />// Author Name is mandatory and needs to be shown in the page. If the content is completed by multiple authors, extra rows can be added, like: article:author” content=”Ian Lau“/>
article:author” content=”Simon Lesser” />// Original publisher name and its URL, this optional entry is used to distinguish original and shared content.
article:published_first” content=“Dragon Metrics Blog, /taking-reporting-automation-to-the-next-level-scheduled-reports-launched/” />
If you are using WordPress, this post provides a handy code snippet that will automatically generate this meta data for you.
This step requires creating an application script to actively push new original content to Baidu, which will allow Baidu to index your new content and verify its originality as quick as possible.
With a Baidu Webmaster Tools account of your verified site, you can get your site’s unique active push protocol URL here. After getting this URL, send it over to your development team and let them create the script for you (more information are available here in Chinese).
Baidu requires new content to be pushed to them immediately after publishing, and claims if this step has done properly your content will be shown with the “Original” tag, and receive ranking benefits within a hour.
By the way, Google adopted something similar to this back in 2010, but we feel the Baidu Spark Project is a well-thought out to combat the content quality issue in China. Here’s to hoping this is a further step in the right direction eliminating scraper sites from search results!